Anna Yeh and Jaclyn Camuglia publish book chapter
Graduate students Anna Yeh and Jaclyn Camuglia publish book chapter on morphogenesis titled Extracellular Tension and Tissue Morphogenesis.

Graduate students Anna Yeh and Jaclyn Camuglia publish book chapter on morphogenesis titled Extracellular Tension and Tissue Morphogenesis.
Jennifer Chu reports on Anthony McDougal’s doctoral thesis, studying butterfly wing scale morphogenesis in Vanessa cardui.
https://news.mit.edu/2024/new-findings-first-moments-butterfly-scale-formation-0626
Original publication here https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8670486/
Congratulations to graduate student, Claudia Vasquez, on passing her qualifying exam.

Congratulations to graduate student, Jonathan Jackson, on passing his qualifying exam.
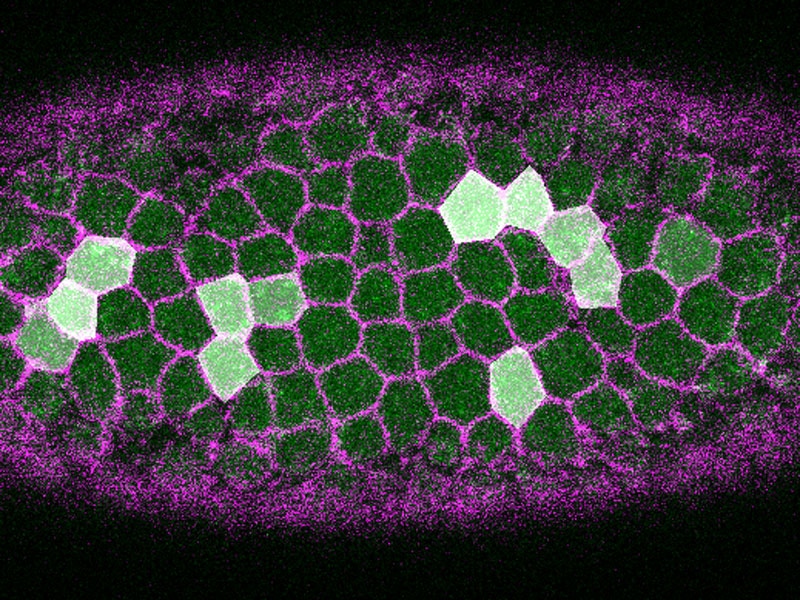
Congratulations Mimi Xie for publishing her work “Loss of Gα12/13 Exacerbates Apical Area-dependence of Actomyosin Contractility” in Molecular Biology of the Cell! Mimi showed how apical actin density can depend on apex size. Suppressing this dependence is important to coordinate contractility across a tissue.

Mingmar joined us this summer from the University of Alabama at Birmingham as our new Technical Associate, welcome!

Congratulations to postdoc, Frank Mason, for the recent publication of his paper, “Apical domain polarization promotes actin-myosin assembly to drive ratchet-like apical constriction” on Nature Cell Biology. In the paper, Mason et al. show that the signals that regulate contractile forces in constricting cells exhibit a spatial organization within the apical domain of the cell. Signals that activate myosin motors are polarized to the center of the apical domain. Actin polymerization in this domain suppresses junctional protein localization, restricting junctional proteins to cell-cell interfaces. Thus, a “radial” cell polarity is established, which is shown to be important for apical constriction.