Nat Clarke published review on Current Biology
Congratulations postdoc Nat Clarke on his review paper on the cytoskeleton, adhesion, and morphogenesis being published in Current Biology.

Congratulations postdoc Nat Clarke on his review paper on the cytoskeleton, adhesion, and morphogenesis being published in Current Biology.

Congratulations Hannah Yevick, for winning the Nano-K 2015 Thesis Prize for interdisciplinary research. This is a national award in France for excellent PhD theses that cross disciplines.
Jennifer Chu reports on Anthony McDougal’s doctoral thesis, studying butterfly wing scale morphogenesis in Vanessa cardui.
https://news.mit.edu/2024/new-findings-first-moments-butterfly-scale-formation-0626
Original publication here https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8670486/
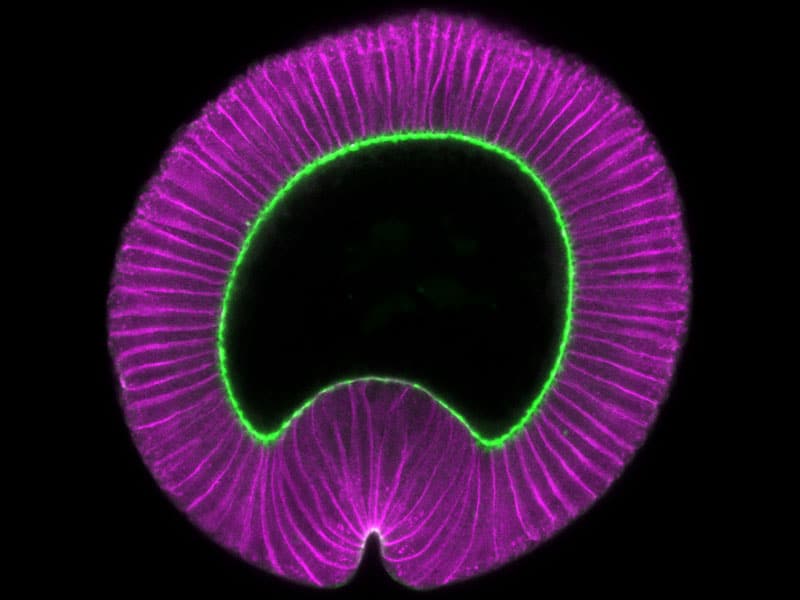
Jonathan comes to us from the Harvard Biophysics PhD program and Mary Ann did her PhD on nuclear movement in muscle.

Congratulations to Hannah Yevick and Clint Ko on submitting their papers. You can read Hannah’s paper titled Structural redundancy in supracellular actomyosin networks enables robust tissue folding, and Clint’s paper titled Microtubules stabilize intercellular contractile force transmission during tissue folding on BioRxiv.

Claudia Vasquez successfully defended her thesis. She gave a stellar seminar to faculty, friends, and colleagues at MIT. Nice job!

Congratulations Mary Ann Collins on publishing review article on plant and animal morphogenesis in Developmental Cell!